Solving in Python with LeNet
In this example, we’ll explore learning with Caffe in Python, using the fully-exposed Solver interface.
Setup
- Set up the Python environment: we’ll use the
pylabimport for numpy and plot inline.
1 | from pylab import * |
- Import
caffe, adding it tosys.pathif needed. Make sure you’ve built pycaffe.
1 | caffe_root = '../' # this file should be run from {caffe_root}/examples (otherwise change this line) |
- We’ll be using the provided LeNet example data and networks (make sure you’ve downloaded the data and created the databases, as below).
1 | # run scripts from caffe root |
Downloading...
Creating lmdb...
Done.
Creating the net
Now let’s make a variant of LeNet, the classic 1989 convnet architecture.
We’ll need two external files to help out:
- the net
prototxt, defining the architecture and pointing to the train/test data - the solver
prototxt, defining the learning parameters
We start by creating the net. We’ll write the net in a succinct and natural way as Python code that serializes to Caffe’s protobuf model format.
This network expects to read from pregenerated LMDBs, but reading directly from ndarrays is also possible using MemoryDataLayer.
1 | from caffe import layers as L, params as P |
The net has been written to disk in a more verbose but human-readable serialization format using Google’s protobuf library. You can read, write, and modify this description directly. Let’s take a look at the train net.
1 | !cat mnist/lenet_auto_train.prototxt |
layer {
name: "data"
type: "Data"
top: "data"
top: "label"
transform_param {
scale: 0.00392156862745
}
data_param {
source: "mnist/mnist_train_lmdb"
batch_size: 64
backend: LMDB
}
}
layer {
name: "conv1"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "data"
top: "conv1"
convolution_param {
num_output: 20
kernel_size: 5
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool1"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv1"
top: "pool1"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "conv2"
type: "Convolution"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "conv2"
convolution_param {
num_output: 50
kernel_size: 5
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "pool2"
type: "Pooling"
bottom: "conv2"
top: "pool2"
pooling_param {
pool: MAX
kernel_size: 2
stride: 2
}
}
layer {
name: "fc1"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "pool2"
top: "fc1"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 500
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "fc1"
}
layer {
name: "score"
type: "InnerProduct"
bottom: "fc1"
top: "score"
inner_product_param {
num_output: 10
weight_filler {
type: "xavier"
}
}
}
layer {
name: "loss"
type: "SoftmaxWithLoss"
bottom: "score"
bottom: "label"
top: "loss"
}
Now let’s see the learning parameters, which are also written as a prototxt file (already provided on disk). We’re using SGD with momentum, weight decay, and a specific learning rate schedule.
1 | !cat mnist/lenet_auto_solver.prototxt |
# The train/test net protocol buffer definition
train_net: "mnist/lenet_auto_train.prototxt"
test_net: "mnist/lenet_auto_test.prototxt"
# test_iter specifies how many forward passes the test should carry out.
# In the case of MNIST, we have test batch size 100 and 100 test iterations,
# covering the full 10,000 testing images.
test_iter: 100
# Carry out testing every 500 training iterations.
test_interval: 500
# The base learning rate, momentum and the weight decay of the network.
base_lr: 0.01
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.0005
# The learning rate policy
lr_policy: "inv"
gamma: 0.0001
power: 0.75
# Display every 100 iterations
display: 100
# The maximum number of iterations
max_iter: 10000
# snapshot intermediate results
snapshot: 5000
snapshot_prefix: "mnist/lenet"
Loading and checking the solver
- Let’s pick a device and load the solver. We’ll use SGD (with momentum), but other methods (such as Adagrad and Nesterov’s accelerated gradient) are also available.
1 | caffe.set_device(0) |
- To get an idea of the architecture of our net, we can check the dimensions of the intermediate features (blobs) and parameters (these will also be useful to refer to when manipulating data later).
1 | # each output is (batch size, feature dim, spatial dim) |
[('data', (64, 1, 28, 28)),
('label', (64,)),
('conv1', (64, 20, 24, 24)),
('pool1', (64, 20, 12, 12)),
('conv2', (64, 50, 8, 8)),
('pool2', (64, 50, 4, 4)),
('fc1', (64, 500)),
('score', (64, 10)),
('loss', ())]
1 | # just print the weight sizes (we'll omit the biases) |
[('conv1', (20, 1, 5, 5)),
('conv2', (50, 20, 5, 5)),
('fc1', (500, 800)),
('score', (10, 500))]
- Before taking off, let’s check that everything is loaded as we expect. We’ll run a forward pass on the train and test nets and check that they contain our data.
1 | solver.net.forward() # train net |
{'loss': array(2.365971088409424, dtype=float32)}
1 | # we use a little trick to tile the first eight images |
train labels: [ 5. 0. 4. 1. 9. 2. 1. 3.]
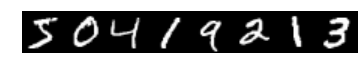
1 | imshow(solver.test_nets[0].blobs['data'].data[:8, 0].transpose(1, 0, 2).reshape(28, 8*28), cmap='gray'); axis('off') |
test labels: [ 7. 2. 1. 0. 4. 1. 4. 9.]

Stepping the solver
Both train and test nets seem to be loading data, and to have correct labels.
- Let’s take one step of (minibatch) SGD and see what happens.
1 | solver.step(1) |
Do we have gradients propagating through our filters? Let’s see the updates to the first layer, shown here as a $4 \times 5$ grid of $5 \times 5$ filters.
1 | imshow(solver.net.params['conv1'][0].diff[:, 0].reshape(4, 5, 5, 5) |
(-0.5, 24.5, 19.5, -0.5)

Writing a custom training loop
Something is happening. Let’s run the net for a while, keeping track of a few things as it goes.
Note that this process will be the same as if training through the caffe binary. In particular:
- logging will continue to happen as normal
- snapshots will be taken at the interval specified in the solver prototxt (here, every 5000 iterations)
- testing will happen at the interval specified (here, every 500 iterations)
Since we have control of the loop in Python, we’re free to compute additional things as we go, as we show below. We can do many other things as well, for example:
- write a custom stopping criterion
- change the solving process by updating the net in the loop
1 | %%time |
Iteration 0 testing...
Iteration 25 testing...
Iteration 50 testing...
Iteration 75 testing...
Iteration 100 testing...
Iteration 125 testing...
Iteration 150 testing...
Iteration 175 testing...
CPU times: user 12.6 s, sys: 2.4 s, total: 15 s
Wall time: 14.4 s
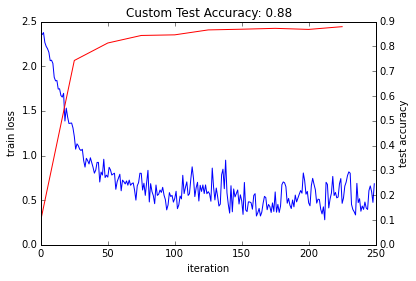
- Let’s plot the train loss and test accuracy.
1 | _, ax1 = subplots() |
<matplotlib.text.Text at 0x7f5199b33610>
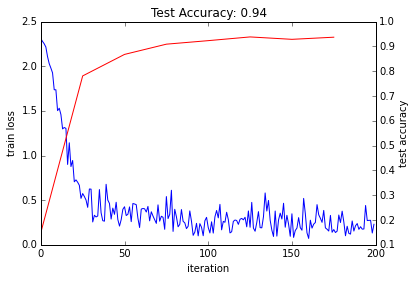
The loss seems to have dropped quickly and coverged (except for stochasticity), while the accuracy rose correspondingly. Hooray!
- Since we saved the results on the first test batch, we can watch how our prediction scores evolved. We’ll plot time on the $x$ axis and each possible label on the $y$, with lightness indicating confidence.
1 | for i in range(8): |

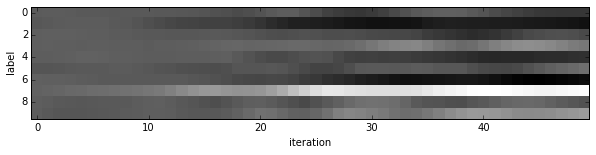

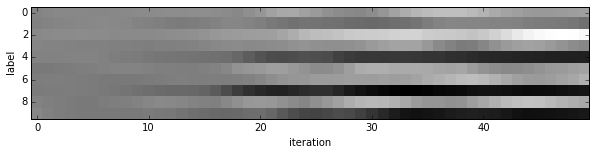



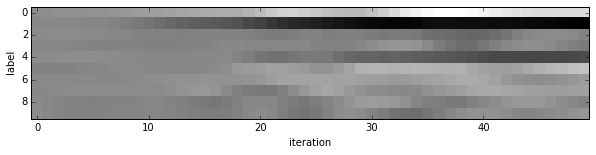

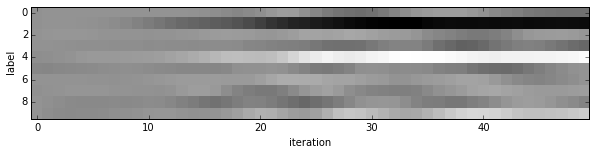


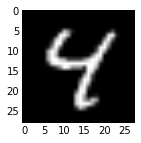
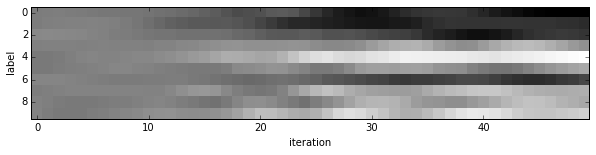

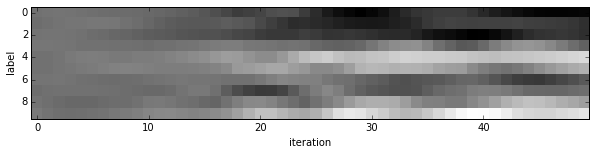
We started with little idea about any of these digits, and ended up with correct classifications for each. If you’ve been following along, you’ll see the last digit is the most difficult, a slanted “9” that’s (understandably) most confused with “4”.
- Note that these are the “raw” output scores rather than the softmax-computed probability vectors. The latter, shown below, make it easier to see the confidence of our net (but harder to see the scores for less likely digits).
1 | for i in range(8): |












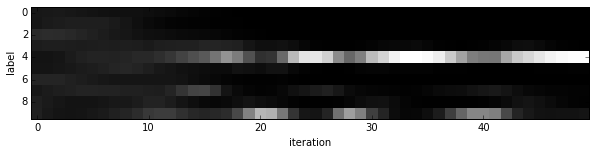


Experiment with architecture and optimization
Now that we’ve defined, trained, and tested LeNet there are many possible next steps:
- Define new architectures for comparison
- Tune optimization by setting
base_lrand the like or simply training longer - Switching the solver type from
SGDto an adaptive method likeAdaDeltaorAdam
Feel free to explore these directions by editing the all-in-one example that follows.
Look for “EDIT HERE“ comments for suggested choice points.
By default this defines a simple linear classifier as a baseline.
In case your coffee hasn’t kicked in and you’d like inspiration, try out
- Switch the nonlinearity from
ReLUtoELUor a saturing nonlinearity likeSigmoid - Stack more fully connected and nonlinear layers
- Search over learning rate 10x at a time (trying
0.1and0.001) - Switch the solver type to
Adam(this adaptive solver type should be less sensitive to hyperparameters, but no guarantees…) - Solve for longer by setting
niterhigher (to 500 or 1,000 for instance) to better show training differences
1 | train_net_path = 'mnist/custom_auto_train.prototxt' |
Iteration 0 testing...
Iteration 25 testing...
Iteration 50 testing...
Iteration 75 testing...
Iteration 100 testing...
Iteration 125 testing...
Iteration 150 testing...
Iteration 175 testing...
Iteration 200 testing...
Iteration 225 testing...
<matplotlib.text.Text at 0x7f5199af9f50>
Reference
History
- 20180808: created.